写在前面
了解到现在 Spring Boot 开发项目非常方便,能省去很多很多配置,所以学着写了一个Demo。主要用了 Spring Boot2、MySQL、JPA。
项目结构
IDEA 现在可以直接新建 SpringBoot 工程,Eclipse 的话,暂时还是需要自己安装插件,就是这个 Spring Tools
搜索安装后就可以直接新建 Spring Boot 工程了
这是最终的项目结构:
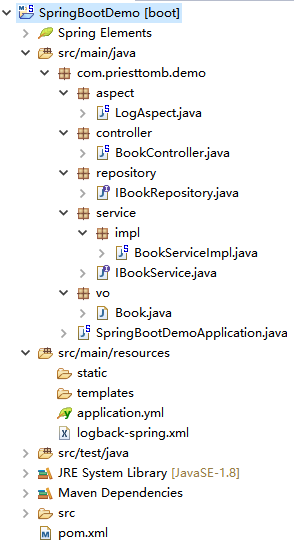
主要代码配置
源码全部丢 github 上去了,可以点这里查看
下面列一些主要的代码和配置
0. application.yml
spring:
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/SpringBootDemo?autoReconnect=true&useSSL=false&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8
username: root
password: mysql
jpa:
hibernate:
ddl-auto: update
show-sql: true
相比原来的 properties 文件,yml 用起来更简便一些,功能都是一样的。
这里的 spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto 配置了 update,可以在启动项目时根据我们配置的 VO 类自动建表、更新表结构。
1. SpringBootDemoApplication.java
package com.priesttomb.demo;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringBootDemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringBootDemoApplication.class, args);
}
}
这个 application 类,就是 Spring Boot 项目的启动入口,不需要像原来那样把工程部署在 Web 服务器上再启动了,因为 Spring Boot 已经内置了 tomcat。
2. BookController.java
package com.priesttomb.demo.controller;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.DeleteMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import com.priesttomb.demo.service.IBookService;
import com.priesttomb.demo.vo.Book;
@RestController
public class BookController {
@Autowired
private IBookService bookService;
/**
* 添加一本书
* @param name 书名
* @param price 书价格
* @return 新书
*/
@PostMapping(value = "/book")
public Book addBook(@RequestParam(value="name") String name,@RequestParam(value="price") Integer price) {
Book book = new Book(name, price);
return bookService.saveBook(book);
}
/**
* 获取所有的书
* @return
*/
@GetMapping(value = "/book")
public List<Book> getAllBooks() {
return bookService.getAllBooks();
}
/**
* 根据书的id获取书
* @param id
* @return
*/
@GetMapping(value = "/book/{id}")
public Book getBookById(@PathVariable("id") Integer id) {
return bookService.getBookById(id);
}
/**
* 根据书的id删除书
* @param id
*/
@DeleteMapping(value = "/book/{id}")
public void delBookById(@PathVariable("id") Integer id) {
bookService.delBookById(id);
}
/**
* 根据书名查书
* @param name
* @return
*/
@GetMapping(value = "/book/name/{name}")
public Book findByName(@PathVariable("name") String name) {
//return bookService.findBook(name);
return bookService.findByName(name);
}
}
随便写了几个方法,这里实现了所谓的 RESTful 服务,就是按照标准,用不同的 HTTP 请求做不同的操作:
-
用 HTTP GET 获取资源
-
用 HTTP POST 创建资源
-
用 HTTP PUT 更新资源
-
用 HTTP DELETE 删除资源
3. IBookRepository.java
package com.priesttomb.demo.repository;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.Query;
import org.springframework.data.repository.query.Param;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import com.priesttomb.demo.vo.Book;
@Repository
public interface IBookRepository extends JpaRepository<Book, Integer>{
//JPA对方法名解析,可以自动生成HQL查询
Book findByName(String name);
@Query("from Book b where b.name=:name")
Book findBook(@Param("name") String name);
}
继承 JpaRepository,然后就可以直接使用常用的方法了,比如 findAll、findById、save、deleteById 之类的
除此之外,JPA 还能解析方法名(前提是写的规范),自动生成 HQL 查询,或者直接用 @Query 来写 JPQL,先简单尝试了下,后面有时间再详细学下这个东西【挖坑
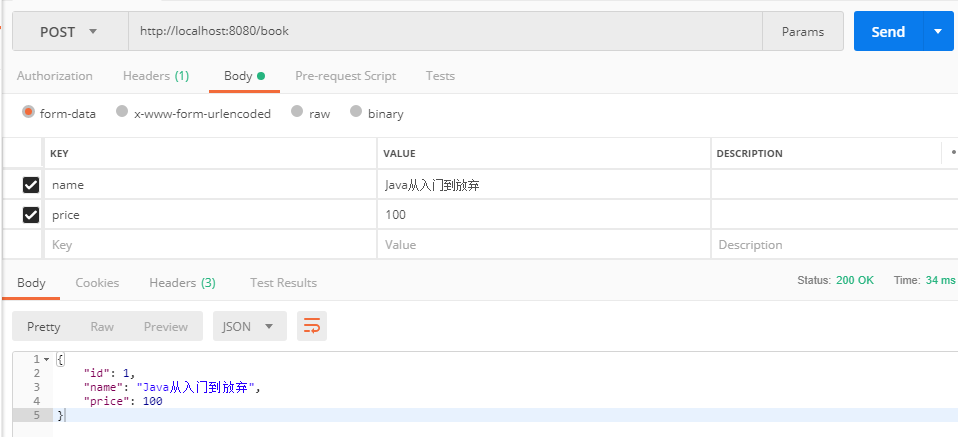
运行测试
emm 用了 Postman,可以方便的选择使用哪种 HTTP 请求,以及设置请求的 Body 内容。
比如: